Welcome back to our financial statement model of Walmart. In this session, we will explore the operational intricacies of Walmart, recognised as one of the largest and most successful retail corporations worldwide. Our examination will entail the initial segment of our comprehensive review of the key elements of Walmart’s 10-K filing, thoroughly assessing the business, its industry context, unique risks, competitive landscape, and emerging trends as reflected in its financial statements.
Let’s get started!

Our objective is to understand the primary drivers behind Walmart’s business operations—specifically, the elements that stimulate its revenue, shape its expenditures, and define its overall financial performance. By dissecting these drivers, we aim to establish a foundational understanding of how Walmart functions as an enterprise. Additionally, as part of this investigation, we will examine Walmart’s most recent 10-K filing, emphasising the essential information necessary to inform our model and enhance our understanding of its financial standing.
Whether you are new to financial modelling or seeking to enhance your existing skills, this series will provide you with the tools to adopt a financial analyst’s perspective.
Walmart
Walmart Inc. stands as a global retail powerhouse and is recognized as the largest company in the world by revenue. It operates an extensive network of hypermarkets, discount department stores, and grocery outlets. Established in 1962 and headquartered in Bentonville, Arkansas, Walmart serves millions of customers on a daily basis through its physical locations and expanding e-commerce platform. With its operations encompassing both domestic and international markets, Walmart’s considerable scale, robust supply chain capabilities, and adaptability render it a fundamental entity within the retail sector and an excellent subject for financial analysis.
We commence our analysis of the company by conducting a thorough examination of Walmart’s most recent 10-K filing to gain an understanding of the business and its operations further.
Business Model and Strategy
This corporation, which is both publicly traded and family-owned, operates as a technology-powered omnichannel retailer that predominantly relies on a brick-and-mortar business model. However, it is noteworthy that its e-commerce segment has been experiencing rapid growth.
Walmart’s business model has transformed the retail corporation into the largest supermarket chain in the United States. As of January 2024, it comprises 10,616 stores—including hypermarkets, supermarkets, and department stores—operating under 56 banners across 27 countries and e-commerce platforms in 10 countries.
The company’s core strategy is to focus on driving growth through price leadership (Every Day Low Prices “EDLP” strategy) while providing a wide selection of goods through a wide range of categories. Through high sales volumes, rapid inventory turnover (often operating with a negative cash conversion cycle, effectively allowing Walmart to operate with supplier financing), efficient supply chains, proprietary technology, and aggressive pricing tactics, Walmart has established a competitive advantage in the market.
Walmart’s operations encompass three reportable segments: Walmart U.S., Walmart International, and Sam’s Club. A more comprehensive examination of these segments will be provided in the next sub-section; however, it is important to acknowledge this information as significant.
Walmart Company Overview
Walmart, whose reporting year ends on 31 January, operates and reports three business segments:
- Walmart U.S.
This is Walmart’s largest segment, and the division operates in the U.S., including all 50 states, Washington D.C., and Puerto Rico. It represents 69% of Walmart’s FY2024 (year-end 31 January 2024) consolidated net sales. Of our three segments, Walmart U.S. has historically contributed the greatest amount to the Company’s net sales and operating income.
Walmart U.S. provides an omnichannel experience to customers, integrating retail stores and eCommerce. The following table provides the approximate size of the retail stores as of January 31, 2024: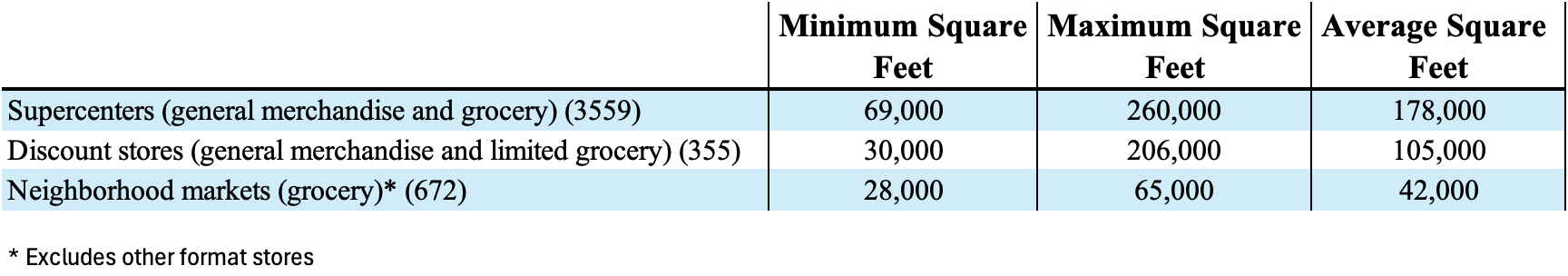
Walmart U.S. does business primarily in three strategic merchandise units: Groceries (dry groceries, snacks, dairy, meat, etc.), general merchandise (entertainment, fashion, home, etc.), and health and wellness (over-the-counter drugs and other medical products, optical services, etc.)
Walmart U.S.’s operations are available to customers through supercentres, discount stores and neighbourhood markets, as well as online or through mobileapplication 24 hours a day. The business’s operations are seasonal to a certain extent due to calendar events and national and religious holidays, with its highest sales volume occurring in the fiscal quarter ending January 31.
Walmart U.S. competes with brick-and-mortar stores, eCommerce, and omnichannel retailers. Each of these landscapes is highly competitive and rapidly evolving, with new business models and the entry of well-funded competitors continuing to intensify this rivalry. Walmart employs numerous strategies and programs designed to meet competitive pressures within our industry. These strategies include the following: Everyday Low Prices (EDLP), Everyday Low Cost (EDLC, commitment to control expenses so cost savings can be passed along to customers), omnichannel offerings such as pickup and delivery to enhance convenience, and the expansion of the business’s ecosystem and the products and services offered.
- Walmart International Segment
Walmart International is our second largest segment and operates in 18 countries outside of the U.S. It represents 18% of Walmart’s FY2024 (year-end 31 January 2024) consolidated net sales. The gross profit rate is slightly lower than that of Walmart U.S. Primarily because of its format and channel mix.
Walmart International includes numerous formats divided into two major categories: retail and wholesale. Its strategy is to create strong local businesses powered by Walmart, which means being locally relevant and customer-focused in each of the markets it operates.
The merchandising strategy for Walmart International is similar to that of our operations in the U.S. in terms of the breadth and scope of merchandise offered for sale. Therefore, Walmart International also does business primarily in groceries, general merchandise, and health and wellness.
Walmart International competes with brick-and-mortar, eCommerce and omnichannel retailers. The business believes that price leadership is a critical part of their business model and continues to progress markets towards an EDLP approach. Additionally, their ability to operate food departments effectively has a significant impact on their competitive position in many of the markets where they operate. - Sam’s Club Segment
Sam’s Club operates in 44 states in the U.S. and Puerto Rico. Sam’s Club is a membership-only warehouse club that also operates samsclub.com. It represents 13% of Walmart’s FY2024 (year-end 31 January 2024) consolidated net sales.
As a membership-only warehouse club, membership income is a significant component of the segment’s operating income. Sam’s Club operates with a lower gross profit rate and lower operating expenses as a percentage of net sales than our other segments.
The following two options are available to members:
Sam’s Club provides an omnichannel experience to members, integrating warehouse clubs and eCommerce. It offers merchandise in the following five merchandise categories: Grocery and consumables, fuel and tobacco, home and apparel, health and wellness, and technology.
Sam’s Club competes with other membership-only warehouse clubs, the largest of which is Costco, as well as with discount retailers, retail and wholesale grocers, etc.
Having developed a comprehensive understanding of Walmart as a business and its operational model, we shall now proceed to examine some of the most significant business risks that the company may face, which could materially impact its operations.
Risk Factors
The risks that will be examined may significantly and negatively impact the business, operational results, financial standing, and liquidity. We will endeavour to condense and consolidate the identified risks presented in the 10-K filing, focusing on those we believe are most likely to have a substantial impact. Should you require a more comprehensive understanding of the various risks that Walmart may encounter, kindly refer to Walmart’s 10-K filing for further details.
Note that Walmart’s business operations could also be affected by additional factors that apply to all companies operating in the U.S. and globally.
- Strategic Risks
“Failure to successfully execute our omnichannel strategy and the cost of our investments in eCommerce and technology may materially adversely affect our market position, net sales and financial performance.”
“If we do not timely identify or effectively respond to consumer trends or preferences, it could negatively affect our relationship with our customers, demand for the products and services we sell, our market share and the growth of our business.”
“We face strong competition from other retailers, wholesale club operators, omni-channel retailers and other businesses which could materially adversely affect our financial performance.” - Operational Risks
“Global or regional health pandemics or epidemics, such as COVID-19, could negatively impact our business, financial position and results of operations.”
“Natural disasters, climate change, geopolitical events, catastrophic and other events could materially adversely affect our financial performance.”
“Risks associated with our suppliers could materially adversely affect our financial performance.” - Financial Risks
“Failure to meet market expectations for our financial performance could adversely affect the market price and volatility of our stock.”
“Fluctuations in foreign exchange rates may materially adversely affect our financial performance and our reported results of operations.” - Legal, Tax, Regulatory, Compliance, Reputational and Other Risks
“Our international operations subject us to legislative, judicial, accounting, legal, regulatory, tax, political and economic risks and conditions specific to the countries or regions in which we operate, which could materially adversely affect our business or financial performance.”
“Changes in tax and trade laws, regulations and interpretations could materially adversely affect our financial performance.”
“Changes in and/or failure to comply with other laws, regulations and interpretations of such laws and regulations specific to the businesses and jurisdictions in which we operate could materially adversely affect our reputation, market position or our business and financial performance.”
It is imperative to examine the risks inherent in Walmart’s business operations, as these risks may elucidate certain trends evident in the company’s financial statements and also aid in forming assumptions regarding Walmart’s future financial performance. The results derived from our financial analysis will serve as the basis for developing our assumptions and comprehending the company’s operational drivers, encompassing both revenue and cost drivers.
The formulation of these assumptions is fundamentally our responsibility as financial analysts. I intend to integrate, to the greatest extent possible, the knowledge acquired from CFA Level 1 and Level 2. Once we have articulated our assumptions and gained a comprehensive understanding of the company’s operational drivers, we will proceed to develop our financial model.
Conclusion
At this point, we have completed the initial portion of our analysis of Walmart’s 10-K filing. Consequently, we should possess a comprehensive understanding of Walmart, its business model and operations, as well as the inherent risks associated with these operations.
In light of this information, the forthcoming week will entail an in-depth evaluation of the latter portion of our analysis regarding Walmart’s 10-K filing, with particular emphasis on the Management’s Discussion and Analysis section. This segment of the statements is pivotal for comprehending the company’s operational drivers and inherent risks, as it elaborates on several line items present in Walmart’s financial statements. Therefore, we will dedicate sufficient time to break down the information meticulously, concentrating on the most significant aspects of this segment.
We truly appreciate you for sticking with us until the end of this reading! Your support means a lot, and we hope this journey has been and will continue to be as educational as it has been enjoyable for you. Until we meet again in the next blog post, take care and see you soon!

Leave a comment